This guide walks you through deploying Rocket.Chat on Kubernetes using Helm. The official Rocket.Chat Helm chart provisions a full workspace built for scalability, resilience, and high availability.
In this guide, you'll learn how to:
To ensure maximum stability, this deployment separates Rocket.Chat from its database instead of using a bundled setup. The architecture allows you to manage, scale, and back up your database layer independently of the application layer. It follows this approach:
Provision an external MongoDB database using the MongoDB Kubernetes Operator. If you already have an external MongoDB instance using a managed service like Atlas, skip steps 2 to 4 and proceed directly to configuring the monitoring stack in step 5.
Configure the monitoring stack with Prometheus and Grafana to enable observability in your workspace.
Deploy Rocket.Chat and connect it to the external MongoDB instance once the database and monitoring stack are healthy.
If you’re currently using our previous bundled setup that relies on the internal chart for MongoDB, refer to Moving from Bitnami to Official MongoDB Chart forum for migration guidance.
Prerequisites
This guide assumes you have a basic understanding of Kubernetes and Helm. Before you begin, verify you have the following server requirements and kubernetes resources.
Server requirements
Domain name: Your domain name must be configured to point to your server’s external IP address.
Kubernetes cluster: A live Kubernetes cluster with
kubectlv1.21 or higher configured.Helm: Helm version 3 must be installed on your server.
Firewall configuration: Verify that your firewall rules allow HTTPS traffic. If you're using a firewall, you may need to whitelist certain URLs to communicate with our cloud services. See the Firewall Configuration guide for a complete list.
Kubernetes resource requirements
The following Kubernetes resources must be configured in your cluster before deployment.
The examples provided here are intended as a guide. Your implementation may vary based on your enviroment and Kubernetes configuration.
Storage Class: A StorageClass is required to provision Persistent Volumes (PVs). If your cluster doesn't have one, you'll need to create it. Run this command to check your storage class:
kubectl get storageclassCopy the name of your StorageClass, you’ll need it to configure the database.
Ingress Controller: An Ingress Controller is essential for routing external traffic to your Rocket.Chat services. This guide uses Traefik as an example.
Add the official Traefik Helm repository:
helm repo add traefik https://traefik.github.io/charts helm repo updateInstall Traefik:
helm install traefik traefik/traefik \ --namespace traefik \ --create-namespaceConfirm that the service has an external IP address by running:
kubectl get svc -n traefik
Certificate manager: If you don’t already have a valid TLS certificate for your domain, configure one using
cert-managerand aClusterIssuer.To facilitate TLS certificate management, install cert-manager by running:
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/cert-manager/cert-manager/releases/download/v1.14.3/cert-manager.yamlConfirm the resources are created:
kubectl get all -n cert-manager
ClusterIssuer: cert-manager requires a ClusterIssuer to automatically issue TLS certificates across the cluster. In this guide, we’ll use Let’s Encrypt.
Save the following to a file named
clusterissuer.yaml:apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1 kind: ClusterIssuer metadata: labels: app.kubernetes.io/instance: use1-cert-manager name: production-cert-issuer # Set your preferred name; referenced in values.yaml later spec: acme: server: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory email: user01@mycompany.com # Replace with your email privateKeySecretRef: name: cert-manager-secret-production # Set your preferred name solvers: - http01: ingress: class: traefikReplace
user01@mycompany.comwith your email address. You can also setprivateKeySecretRef.nameto your prefered name.Create the resource:
kubectl apply -f clusterissuer.yamlVerify the ClusterIssuer was deployed and the secret was created succesfully:
kubectl get clusterissuer kubectl get secret -n cert-manager
The Rocket.Chat Helm chart requires your Kubernetes cluster to support dynamic persistent volume (PV) provisioning. Local Kubernetes distributions such as Kind, K3s, and Minikube often ship without a storage provisioner enabled. In these cases, you can do either of the following:
Disable the bundled MongoDB chart and connect to an external MongoDB instance
Install a storage provisioner that is compatible with your environment
Once you've confirmed that all prerequisites are met, continue with the next steps to deploy a Rocket.Chat workspace using Kubernetes.
Step 1: Add the Helm chart repositories
Add the official Rocket.Chat and MongoDB Helm repositories:
helm repo add mongodb https://mongodb.github.io/helm-charts
helm repo add rocketchat https://rocketchat.github.io/helm-charts
helm repo updateYou should see confirmation that the repositories were added successfully.
Step 2: Install MongoDB Kubernetes operator
With the required kubernetes resources in place, the next step is to install the MongoDB Kubernetes operator. This operator is responsible for managing MongoDB lifecycle tasks, including provisioning, scaling, and health reconciliation.
Create a namespace:
kubectl create namespace rocketchatThis guide uses
rocketchatas the namespace. You can change it to a different name, but ensure you use the configured name in subsequent steps.Install the MongoDB operator:
helm install mongodb-kubernetes-operator mongodb/mongodb-kubernetes \ -n rocketchatAvoid installing the CRDs separately. The operator chart manages them automatically.
Wait for the MongoDB operator to be ready:
kubectl rollout status deployment/mongodb-kubernetes-operator \ -n rocketchat \ --timeout=300s
Step 3: Configure database secrets and replica set
Now that the MongoDB operator is running, you can define the MongoDB resources it will manage. This step provisions a highly available MongoDB replica set and configures authentication for Rocket.Chat.
Create a file named
mongodb-secrets.yamlwith the following contents for the MongoDB secrets :--- apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: namespace: rocketchat name: mongodb-admin-password type: Opaque stringData: password: <your-secure-admin-password> --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: namespace: rocketchat name: mongodb-rocketchat-password type: Opaque stringData: password: <your-secure-rocketchat-password> --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: namespace: rocketchat name: metrics-endpoint-password type: Opaque stringData: password: <your-secure-prometheus-password> --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: namespace: rocketchat name: admin-scram-credentials type: Opaque stringData: username: admin password: <your-secure-admin-password> --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: namespace: rocketchat name: rocketchat-scram-credentials type: Opaque stringData: username: rocketchat password: <your-secure-rocketchat-password>Replace the following placeholder passwords with secure values:
<your-secure-admin-password>,<your-secure-rocketchat-password>,<your-secure-prometheus-password>.Apply the secrets:
kubectl apply -f mongodb-secrets.yamlCreate a file named
mongodb-community.yamlwith the following contents for the MongoDB community resource:This example creates a single node replica set. You can configure additional replica sets as needed to ensure chat history and user data remain available if a node fails.
apiVersion: mongodbcommunity.mongodb.com/v1 kind: MongoDBCommunity metadata: name: mongodb namespace: rocketchat spec: members: 1 #Update to your desired number of replicaSet type: ReplicaSet version: "8.2.3" security: authentication: modes: ["SCRAM"] tls: enabled: false users: - name: admin db: admin passwordSecretRef: name: mongodb-admin-password scramCredentialsSecretName: admin-scram-credentials roles: - name: root db: admin - name: rocketchat db: rocketchat passwordSecretRef: name: mongodb-rocketchat-password scramCredentialsSecretName: rocketchat-scram-credentials roles: - name: readWrite db: rocketchat prometheus: username: prometheus-username passwordSecretRef: name: metrics-endpoint-password statefulSet: spec: volumeClaimTemplates: - metadata: name: data-volume spec: accessModes: ["ReadWriteOnce"] storageClassName: <your-storage-class> resources: requests: storage: 50Gi template: spec: containers: - name: mongod resources: limits: cpu: 1500m memory: 1Gi #Configure the limits memory as required requests: cpu: 500m memory: 1Gi #Configure the requests memory as requiredReplace
<your-storage-class>with your actual StorageClass name.Update
spec.membersto your desired number of replica set.Configure
limits.memoryandrequests.memoryas required for your workspace.
Apply the MongoDB resource :
kubectl apply -f mongodb-community.yaml
Step 4: Verify the MongoDB setup
After MongoDB is deployed, validating its health and connectivity ensures the database is ready for application traffic. This step confirms the pods, services, and authentication are functioning as expected.
After it’s deployed, wait for the MongoDB to be ready:
kubectl wait --for=condition=ready pod -l app=mongodb-svc \ -n rocketchat \ --timeout=300sConfirm the pod status:
kubectl get pods -n rocketchat | grep mongodbVerify the service endpoints:
kubectl get endpoints mongodb-svc -n rocketchatYou should see the MongoDB pod's IP address listed. If endpoints are empty, the service selector isn't matching the pod labels correctly. Refer to Kubernetes Deployment FAQ for troubleshooting steps.
Validate MongoDB Health
Before deploying Rocket.Chat, ensure the database is healthy:
kubectl exec -it mongodb-0 -n rocketchat -- \
mongosh admin --eval "db.adminCommand('ping')"Expected output: { ok: 1 }.
Build the MongoDB connection string
Extract the rocketchat user password and generate the MongoDB connection string:
MONGO_PASSWORD=$(kubectl get secret mongodb-rocketchat-password \ -n rocketchat -o jsonpath='{.data.password}' | base64 -d) echo "MongoDB URI:" echo "mongodb://rocketchat:${MONGO_PASSWORD}@mongodb-0.mongodb-svc.rocketchat.svc.cluster.local:27017/rocketchat?authSource=rocketchat&replicaSet=mongodb"The generated connection string should be similar to this format:
mongodb://rocketchat:testrc123@mongodb-0.mongodb-svc.rocketchat.svc.cluster.local:27017/rocketchat?authSource=rocketchat&replicaSet=mongodbSave the generated MongoDB connection string, you’ll need it to connect to Rocket.Chat later.
Step 5: Deploy the monitoring stack
To effectively monitor your workspace, the official Rocket.Chat Helm chart includes Prometheus for collecting metrics, Loki for log collection, and Grafana for visualizing metrics and logs through dashboards. This setup allows you to visualize key metrics, track performance, and gain insights into the health of your Rocket.Chat instance.
Create a file named
values-monitoring.yamland add the following configuration:ingress: enabled: true ingressClassName: "traefik" # Specify the installed ingress controller in the K8s cluster tls: true grafana: enabled: true host: "domain.xyz" path: "/grafana"Update
domain.xyzwith your actual domain name.Set the
ingressClassNameto the ingress controller you are using.
Install the monitoring stack:
helm install monitoring -f values-monitoring.yaml rocketchat/monitoring -n rocketchatA successful output should look like this:
Step 6: Configure Rocket.Chat
With database and monitoring stack running, the next step is to define how Rocket.Chat should run in your cluster. These configuration values control image versions, ingress, TLS, and service behavior.
Create a
values.yamlfile to define your deployment configurations. This file specifies how Helm should configure your Rocket.Chat workspace.Below is an example configuration to use for your deployment:
image: pullPolicy: IfNotPresent repository: registry.rocket.chat/rocketchat/rocket.chat tag: <release> # Set the Rocket.Chat release mongodb: enabled: false externalMongodbUrl: "<enter-external-mongodb-uri>" microservices: enabled: true replicaCount: 1 host: <domain.xyz> ingress: enabled: true ingressClassName: traefik annotations: cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: production-cert-issuer tls: - secretName: rckube hosts: - <domain.xyz> nats: cluster: name: rocketchat-nats-clusterReplace
<release>with the Rocket.Chat version you want to deploy.Connect the external MongoDB by replacing
<enter-external-mongodb-uri>with the connection string you saved in step 4.Update
<domain.xyz>with your actual domain name.Set the
ingressClassNameto the ingress controller you are using.If you’ve configured a certificate manager and ClusterIssuer for TLS, specify your ClusterIssuer name and a
secretNamefor TLS. If you already have a valid certificate or do not wish to use TLS, theannotationsandtlsvalues can be omitted.Explore additional deployment configuration options you can set in your
values.yamlfile to suit your workspace requirements.
While microservices is enabled in this configuration, it uses a single replica which is suitable for Community workspaces. To scale your workspace with multiple replicas, see our Microservices documentation.
Step 7: Deploy Rocket.Chat
Once configuration is finalized, you can launch the Rocket.Chat deployment.
Install Rocket.Chat with the configurations you defined in
values.yaml:helm install rocketchat -f values.yaml rocketchat/rocketchat -n rocketchatIf your deployment is successful, you’ll get a response similar to the following:
Wait for the Rocket.Chat to be ready:
kubectl rollout status deployment/rocketchat-rocketchat \ -n rocketchat \ --timeout=300sVerify that the pods for your deployment are running:
kubectl get pods -n rocketchatYou should see a list of pods in the
Runningstate, similar to the example below: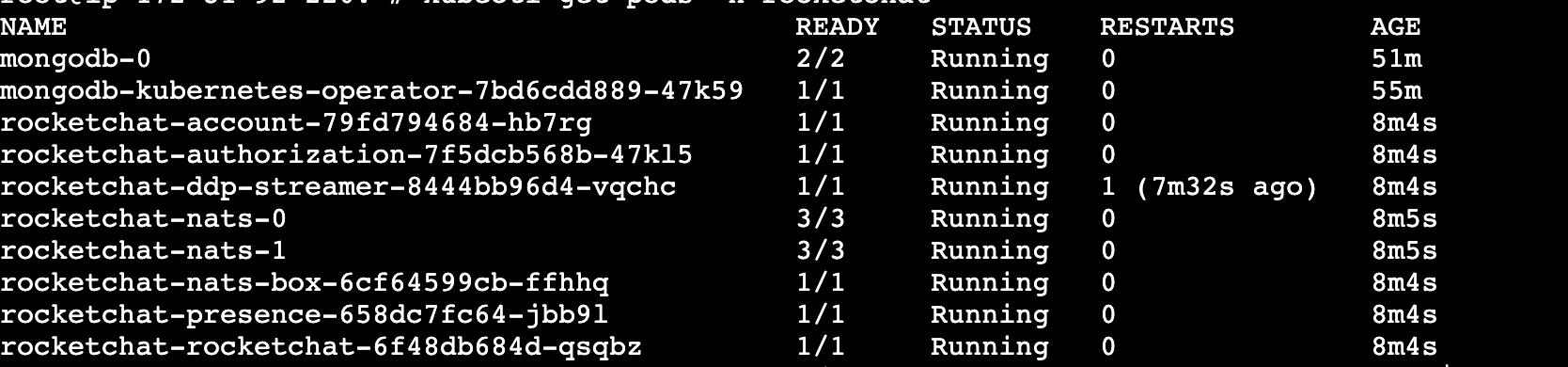
Your output may vary depending on your configuration.
Check Rocket.Chat logs to confirm it's started:
kubectl logs deployment/rocketchat-rocketchat -n rocketchat | grep -A 15 "SERVER RUNNING"You should see an output like:
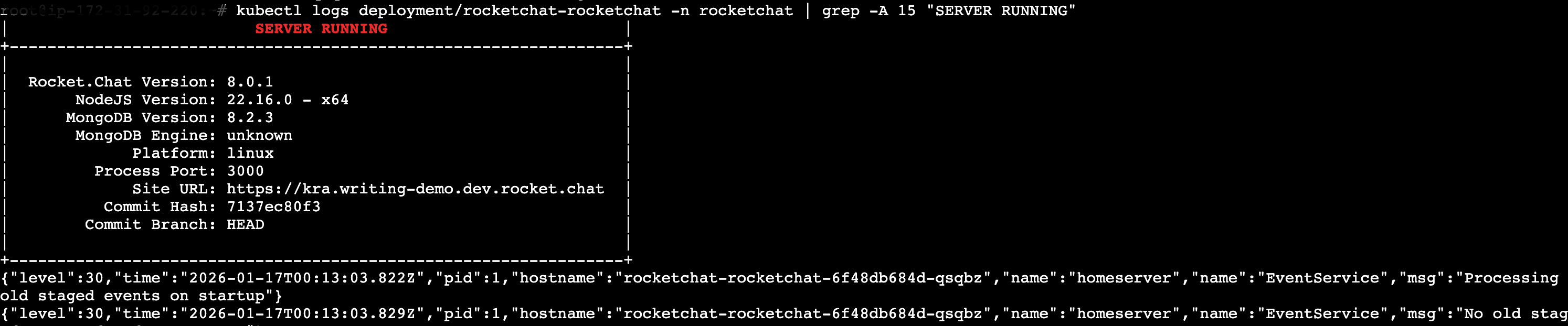
If you encounter any issues with your deployment, refer to the Kubernetes Deployment FAQ.
Step 9: Access your Rocket.Chat workspace
After a few minutes, your Rocket.Chat workspace will be accessible at the domain you configured (e.g., https://domain.xyz).
Follow the on-screen prompts to complete the initial setup and configuration of your workspace. During this process, your workspace and email will be registered to the Rocket.Chat Cloud portal, where you can manage your subscriptions.
Access monitoring dashboard
A Grafana dashboard will also be available at the path you configured (e.g., https://domain.xyz/grafana). To log in, use the following default credentials:
User:
adminPassword:
admin
You’ll be prompted to set a new password after your first login.
For more details on how to monitor your workspace metrics and logs, refer to the Monitor Workspace Logs and Metrics guide.
Step 10: Update file storage
Rocket.Chat stores file uploads using GridFS by default. While this doesn't require extra setup, it's not ideal for production because it increases database load and reduces scalability performance. Rocket.Chat highly recommends using a dedicated object storage service such as Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage (GCS), or MinIO. Refer to the File Uploads guide for detailed instructions on configuring your preferred file storage solution.
Next steps
Congratulations! You have successfully deployed your Rocket.Chat workspace on Kubernetes. Your workspace is now live and ready to use. Next, check out the following resources to continue using your workspace:
User Guides: Learn the basics of your Rocket.Chat account, the types of rooms, and how to communicate with your workspace users.
Workspace Administration: Administrators and owners can set and manage various configurations.
Marketplace: Explore the available apps to enhance your workspace.
Updating Rocket.Chat on Kubernetes
Before you proceed, consult the general guidelines for updating MongoDB.
To update your Rocket.Chat workspace to a new version,
Update the
image.tagfield in yourvalues.yamlfile with the desired release:
image:
tag: <release>Replace <release> with the Rocket.Chat release number you want. For details about available Rocket.Chat versions, refer to Rocket.Chat release notes.
After updating the image, execute the following command:
helm upgrade rocketchat -f values.yaml rocketchat/rocketchat -n rocketchatAfter a few minutes, return to your workspace subscription to verify the updated Rocket.Chat version.
For more information on updating Rocket.Chat, refer to this issue. Whenever you update your
values.yamlfile, always run thehelm upgradecommand above to apply the changes to your workspace.
Updating MongoDB version on Kubernetes
Before upgrading MongoDB, confirm all of the following:
Check the release notes to verify that your target MongoDB version is supported by your current Rocket.Chat release.
Avoid skipping major versions. For example, to move from 4.4 to 6.0, you must upgrade to 5.0 first, ensure it is stable, and then proceed to 6.0.
The database
featureCompatibilityVersionmust be compatible with the target MongoDB version. If you are running MongoDB 5.0 but yourfCVis still set to 4.4, an upgrade to 6.0 will fail.
To update your MongoDB version, run this command:
kubectl patch mongodbcommunity mongodb -n rocketchat \
--type='json' -p='[{"op": "replace", "path": "/spec/version", "value":"<mongodb-version>"}]'Replace <mongodb-version> with the version of MongoDB you want to update to.
Additional steps
Uninstalling Rocket.Chat on Kubernetes
To uninstall and delete the Rocket.Chat deployment, use the command:
helm delete rocketchat -n rocketchatYou said
Set Rocket.Chat deployment environment variable on Kubernetes
Enviroment variables define key settings that influence or control how your workspace is deployed and configured. To set an environment variable in Kubernetes,
Open your
values.yamlfile:nano values.yamlAdd the environment variable under
extraEnv. For example, to override the SMTP Host setting, add:extraEnv: - name: OVERWRITE_SETTING_SMTP_Host value: "my.smtp.server.com"Finally, upgrade your deployment to apply the new changes:
helm upgrade rocketchat -f values.yaml rocketchat/rocketchat -n rocketchat
For a full list of available environment variables, refer to Deployment Environment Variables.
Logging your deployment
To verify that the pods for your deployment are running:
kubectl get pods -n rocketchatTo view the logs for a specific Rocket.Chat pod:
kubectl logs -n rocketchat <pod-name>To stream real-time logs from a running Rocket.Chat pod:
kubectl logs -n rocketchat -f <pod-name>This helps in tracking ongoing events and debugging issues as they occur.
To check MongoDB replica set status:
kubectl exec -it mongodb-0 -n rocketchat -- \ mongosh admin --eval "rs.status()"Get the service details for the deployment:
kubectl get svc -n rocketchat
If you encounter further issues with your deployment, refer to the Kubernetes Deployment FAQ.
Scale MongoDB replicas
Since you’re using the MongoDB Community Operator, scaling the database is handled by patching the Custom Resource. This ensures the operator manages the safe addition of new replica members.
To scale MongoDB, update the number of MongoDB members in the ReplicaSet with this command:
kubectl patch mongodbcommunity mongodb -n rocketchat \
--type='json' -p='[{"op": "replace", "path": "/spec/members", "value": <replica-set-number>}]'Replace <replica-set-number> with the number of replica sets you want to scale to.
To further explore and enhance your workspace on Kubernetes, consider the following next steps: